Ordnance Survey releases new roof data for over 40 million buildings
The new information will enhance an already comprehensive buildings dataset
Press Office
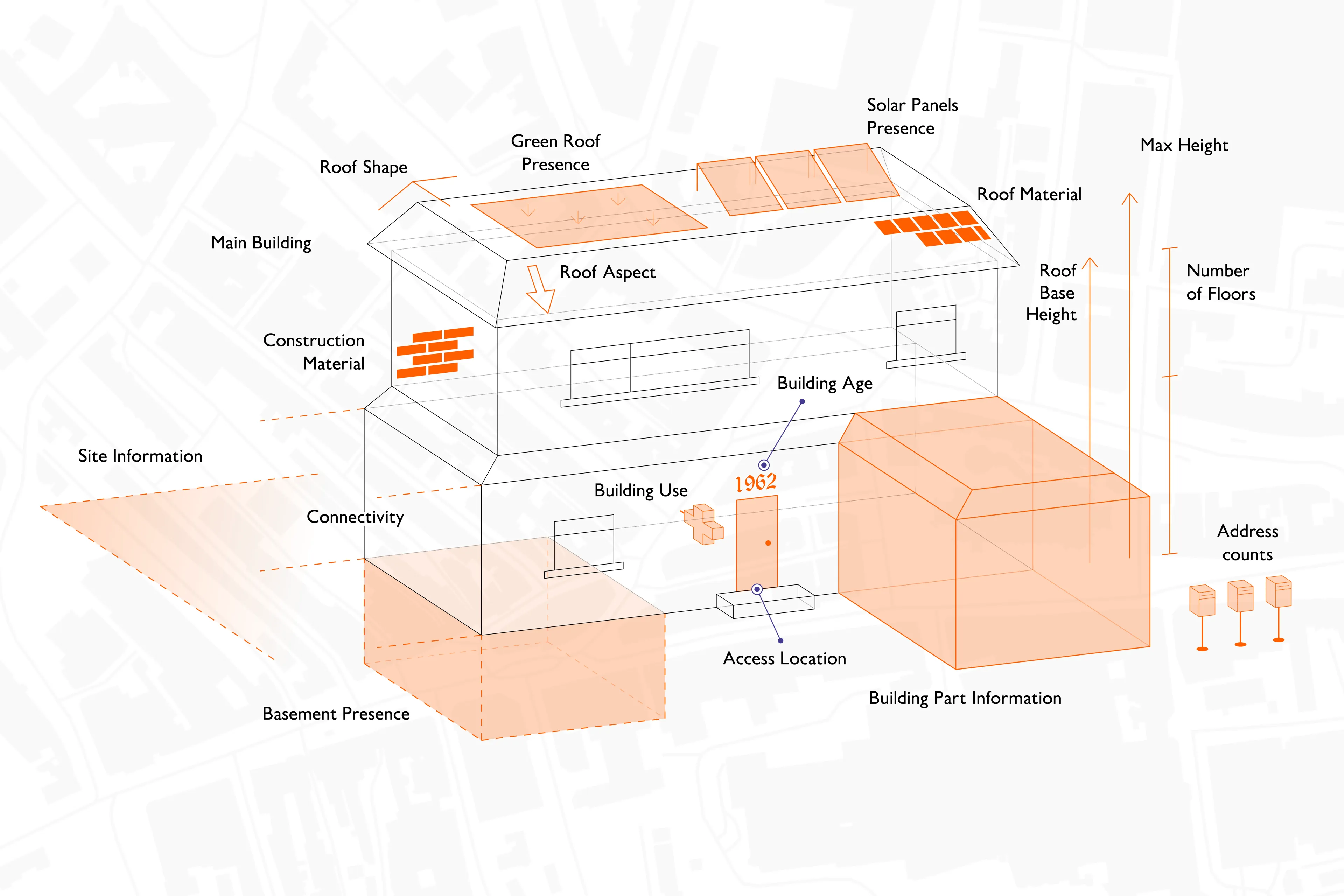
The new roof attributes introduce unprecedented insights into roof shape, aspect, material, green roofs and presence of solar panels. It was almost entirely captured using automated feature extraction, utilising Machine Learning methodologies in some processes.
The OS NGD already holds a vast amount of information on buildings, including their use (e.g., commercial, retail, residential), construction material, age, number of floors (47 million in total), address count, and basement presence.
All of these features are available in the OS NGD Buildings theme alongside the brand new roof enhancement data. They can be cross-referenced with other OS NGD themes such as Address and Land Use to unlock valuable insights that can support projects and businesses across the public and private sector.
"This is the most significant collection of new and existing data for buildings in the OS National Geographic Database since it was created in 2022. With the addition of the new roof data, OS can support so many different sectors with achieving key insights and deliverables - from insurance and property to local authorities under pressure to meet biodiversity net gain targets. And we’re not stopping here—more building datasets are in the pipeline for future release."
Roof shape and aspect – to support risk assessment and retrofitting
OS’s new roof data includes:
- Roof shape: identifying whether a roof is flat or pitched, which helps assess water ingress risk for insurance purposes and supports carbon net zero initiatives, retrofitting and solar panel suitability.
- Roof aspect: determining the predominant orientation in eight directions (eg north, northeast, east), supporting green energy planning and wind and storm risk modelling for insurers.
The enhanced roof data allows for better building representation by modelling roof shape, benefitting industries like architecture and urban planning.
Roof material – from fire risk to green energy planning
OS now provides data on the predominant roof materials for 25 million addressable buildings, categorising them as waterproof membrane/concrete, fabric, glass/polycarbonate, green roof, metal, thatch, or tile/stone/slate (on 92% of buildings).
This data will support multiple sectors to:
- Help identify fire risks (e.g. listed buildings and thatched roofs).
- Support green energy solutions by mapping solar panel and green roof potential.
- Aid in heat loss modelling for energy efficiency planning and maintenance.
- Improve mobile network planning, helping determine suitable locations for infrastructure.
Interestingly, only 0.1% of British buildings have thatched roofs. The area with the highest total number is Sidmouth, East Devon.

Green roofs – invaluable for sustainability and biodiversity projects
A green roof is defined as at least partially covered with vegetation, usually specifically installed on a waterproof membrane. This new dataset will be invaluable for sustainability and biodiversity projects, supporting:
- Urban biodiversity (e.g. shelter for pollinators, air filtration, oxygen generation).
- Energy efficiency (e.g. reduced urban heat islands, increased cooling system performance).
- Enhanced solar panel efficiency.
- Improved retail and commercial spaces, making urban environments more attractive.
Solar panel mapping - for energy efficient ratings and renewable incentives programmes
For the first time, OS has identified the presence of solar panels, revealing that 5% (nearly 1.3 million) of buildings across Britain have them, and are mostly domestic. Scotland has the highest proportion of domestic solar panels. The top three districts in Britain are Stirling (15%), South Cambridgeshire (14%), and Peterborough (13%).
This data will revolutionise market analysis and investment strategies for:
- Property valuation and energy efficiency ratings.
- Green financing and investment.
- Renewables incentives programmes.
- Carbon footprint analysis for businesses and residential areas.
New data on access points to key public buildings
Also being introduced to the OS NGD Buildings theme, is the mapping of pedestrian and vehicle access points to major public buildings. The data is set to enhance emergency planning and response times, improve situational awareness, and help wheelchair users navigate key public buildings more easily.
The data includes access points to:
- Hospitals
- Sports arenas (5,000+ capacity)
- Railway stations, airports, and ferry terminals
- Shopping centres (50+ units)
- Conference centres (500+ capacity)
- Concert venues (1,000+ capacity)
These 88,000+ access features provide a new level of detail including:
- Access type (e.g. public, private, emergency).
- Level (e.g. above/below ground).
- Accessibility details (e.g. ramps, obstructions).
Also in the new update is access purpose for the sites containing those key public buildings above. This is contained within the OS NGD Land Use theme.
Other new data in this release includes building height enhancements, streetlights, tunnels, three additional land use site descriptions (beaches, wind farms, military training areas) and additional information in the OS NGD Geographical Names theme.
The new location data has been released as part of the Public Sector Geospatial Agreement (PSGA). The PSGA is a contract between Government Digital Service, managed on behalf of the UK Government, and OS for the provision of geospatial data and services to the emergency services and wider public sector organisations.
Sharing the latest news about OS. We can license you to use OS maps in print, online and film format. For more information and resources for journalists, bloggers and media professionals, email pressoffice@os.uk or call 023 8005 5565.
What is the OS NGD?
The OS NGD is a single store of all Ordnance Survey’s authoritative data for Great Britain. The OS NGD delivers the richer data you need for better analysis and our download service, OS Select+Build, makes it easier to find, package and analyse the data you need, such as address and building data for emergency planning.